Bone and Muscle Health
Persons with disabilities should be encouraged to promote bone and muscle health with physical activity and having 2-3 servings of dairy or a dairy alternative
3.1 Physical Activity Recommendations:
Adults who are physically active are healthier, feel better, and are less likely to develop many chronic diseases than adults who are inactive. For adults, regular physical activity can provide both immediate benefits (e.g., boost mood, reduce stress, improve sleep) and long-term benefits (e.g., improved bone health and reduced risk of many diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, depression, dementia, and many types of cancer). Adults should move more and sit less throughout the day. Some physical activity is better than none.
To attain the most health benefits from physical activity, adults need at least 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, like brisk walking or fast dancing, each week.
Adults also need muscle-strengthening activity, like lifting weights or doing push-ups, at least 2 days each week.
3.2 Recommendations for Adults:
Some examples of exercises: weight bearing-walking, climbing stairs, tennis, jumping rope, jogging, hi-impact aerobics, dancing, chair dipping (for weight-bearing on arms), and hiking. Resistance exercises – such as lifting weights – can also strengthen bones. Other exercises such as swimming and bicycling can help build and maintain strong muscles and have cardiovascular benefits, but they are not the best way to exercise your bones.
For more information and ideas on exercise and physical activity visit the following resources:
NCHPAD Exercise and Fitness Resources
CDC’s Recommendations for Physical Activity for People with Disabilities
3.3 Recommendations for Children:
Walking, holding yoga positions, hanging from monkey bars or jungle gyms, pushing/pulling a box of toys, planking with straight arms or elbows, and crawling on all fours.
“Some great exercises for children with physical disabilities are:
- Boxing.
- Swimming.
- Water Aerobics.
- Boxing and swimming promote increased upper arm function and strength as well as cardiovascular endurance.
Fun activities include programs such as the Nintendo Wii and the Switch! These game consoles offer activities using just your hands so those who are in a wheelchair can participate.
Games include
- Boxing.
- Tennis.
- Baseball.
- Bowling.
This is a great way to get the entire family involved and keep your child moving!
It is important to note that children with physical disabilities can participate in most sports. Sports can be fun to play and can give your child an emotional boost.
To find sports your child can engage in, ask other parents, teachers, doctors, and therapists as they are often aware of programs available to help your child. Once you find a program, always have your child try it out. Not all programs will work for everyone. Find one that your child feels comfortable joining and enjoys doing.” Exercise Right Physical Disabilities
3.4 Dairy or dairy alternative
- Dairy or dairy alternatives contain vital nutrients that can help promote and optimize musculoskeletal health.
- Dairy sources include:
- Regular, Skim, and 2%, lactose-free milk.
- Yogurt, Greek Yogurt.
- Alternatives/Milk Substitutes have lower fat and protein: Rice Milk, Oat Milk, Almond Milk, Coconut Milk, Cashew Milk, Flaxseed Milk, Hemp Milk.
- It is important to note that the USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans do not consider products sold as “milks” made from plants as contributing to the dairy group recommendation as their nutrition content is not similar to dairy milk or fortified soy beverages. These “milks” include: almond, rice, coconut, oat, and hemp milk.
- The table below highlights the nutrient composition of milk and milk substitutes.
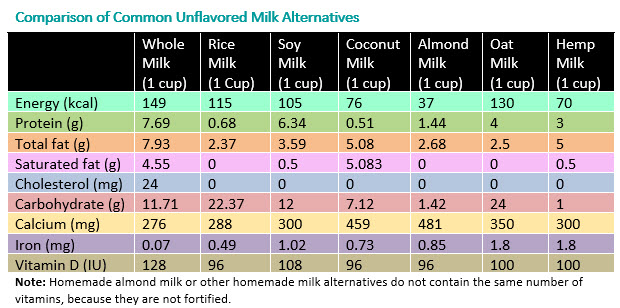
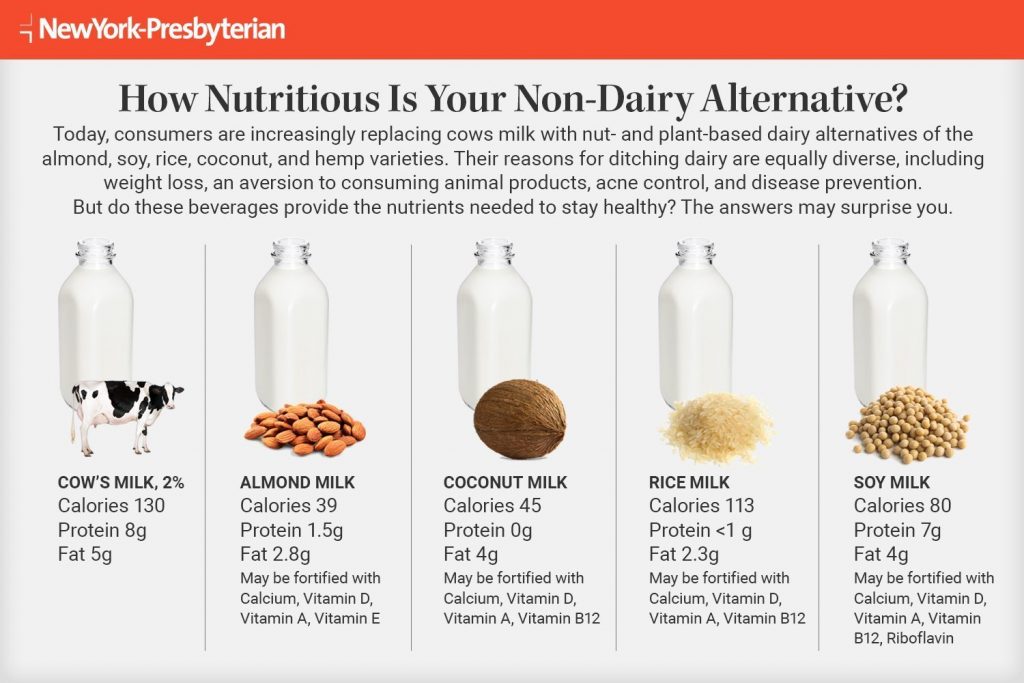
- Alternatives/Yogurt Alternatives: Coconut Milk Yogurt, Almond Milk Yogurt, Soy Milk Yogurt, Hemp Yogurt.
- Alternatives/Cheese Alternatives that are non-dairy:
- Soft Cheese Substitutes
- Cottage Cheese.
- Mascarpone.
- Cashew Almond (Non-Dairy Alternative).
- Hung Curd.
- Tofu.
- Ricotta Cheese.
- Gervais.
- Sour Cream.
- Alternatives/ Butter: Vegetable Oil Blends, Coconut Butter,
- Cultured Vegan Butter, Nut Butters.
- Alternatives/Heavy Cream Substitutes.
- Soy milk with olive oil.
- Butter and milk.
- Evaporated milk.
- Cashew Cream.
- Pureed tofu or white beans.
- Oil and dairy-free milk.
- Brown rice and low-fat milk.
- Alternatives for Sour Cream
- Greek yogurt (Dairy-Based Substitutes).
- Cottage Cheese (Dairy-Based Substitutes).
- Creme Fraiche (Dairy-Based Substitutes).
- Buttermilk (Dairy-Based Substitutes).
- Coconut Milk (Non-Dairy Alternatives).
- Cashews (Non-Dairy Alternatives).
- Soy (Non-Dairy Alternatives).
- Alternatives for Ice Cream/Sherbets:
- Creamy ice creams are made from non-dairy milks, including coconut milk and soy milk.
- Sorbets, which never have dairy in them.
- Home- made-like-ice cream-like desserts made from blending frozen bananas.
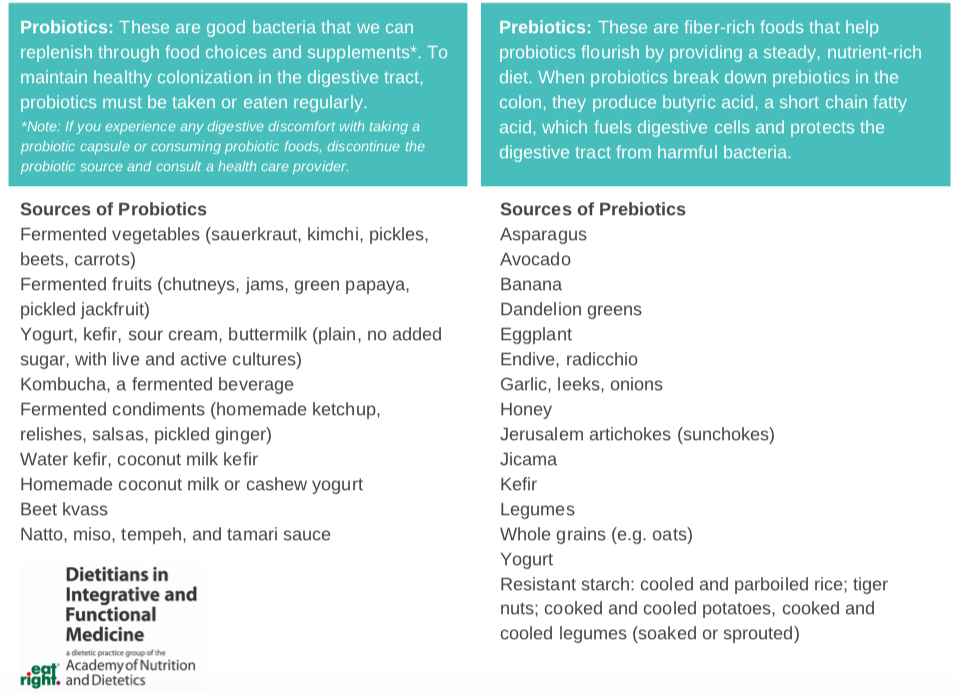
3.5 Probiotic Foods: